Cisco Router
◾ Router : 서로 다른 네트워크 연결 장치 (어떤 패킷이 어느 포트로 나갈지 계산하는 것)
• 물리적인 환경(Link layer)과는 무관하게 네트워크 ID(네트워크 주소)가 다른 네트워크를 연결한다.
• 라우팅이 지원되는 프로토콜에서 사용 가능하다.
- IP, IPX 등
• 라우팅을 제공하는 장치는 라우터 이외에도 거의 모든 네트워크가 지원되는 OS에서 가능하다.
- 리눅스, 유닉스, 윈도우 등등
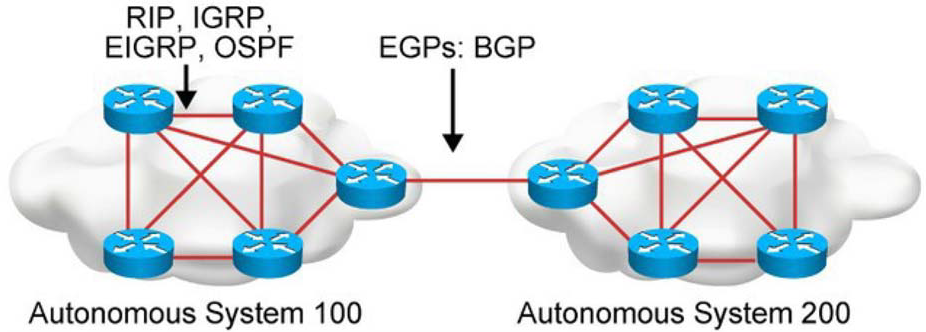
◾ Routing protocol
• static
• RIP
• OSPF
• IGRP
• EIGRP
• BGP
* TCP/IP 에서 Gateway : 우리 네트워크에서 다른 네트워크로 나갈때 거치는 지점 (ex. 라우터, 방화벽)
◾ Distance Vector
• Hop count base
• RIP
◾ Link-State
• Cost base
• OSPF, IS-IS
◾ Advanced Distance Vector
• EIGRP
◾ Classful > 지금 사용X
• Subnet mask를 교환하지 않는다. (*subnet mask : ip주소에서 네트워크 주소를 결정 짓는것)
• RIP, IGRP (인터넷 초창기에 사용)
◾ Classless
• Subnet mask를 교환한다.
• RIPv2, OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS, BGP (현재 사용)
◾ Bast path : Administrative Distance
• 동일 목적지에 대한 경로가 서로 다른 프로토콜에 의해 수집될 경우 Protocol에 부여된 우선 순위에 따라 Bast path를 결정한다.
| Route Source | Default Distance |
| Connection intface Static route EIGRP IGRP OSPF RIP Enternal EIGRP Unknown |
0 01 90 100 110 120 170 255(never be used) : 경로 찾을 수X |
◾ 다양한 구조의 네트워크에서 Router가 사용되며 최근에는 방화벽과 라우터가 하나의 장비로 구성되는 경우도 있다.
(방화벽과 라우터는 다른 장비)
◾ 게이트웨이
• 라우터
• 방화벽
◾ 초기 인터넷에서 모든 단위 네트워크의 구분에 라우터가 이용되었으나 IP 고갈등의 문제로 ISP의 상당수 서비스는 라우터를 기반으로하지 않는다.
• 중소규모의 최종 사용자 네트워크에 라우터가 점점 쓰이지 않는다.
• Router간 연결이나 ISP 연결 환경이 serial에서 광이나 UTP와 같은 LAN 매체로 바뀌고 있다.
정적(Static) 라우팅
◾ 정적 라우팅
: 모든 경로에 대한 정보를 직접 관리자가 입력해주는 방식
• 단순 경로 네트워크나 단일 외부 경로를 가진 최종 사용자 네트워크에 매우 유용하다.
• 라우터 장치 이외에 리눅스나 유닉스 윈도우즈등의 OS에서도 기본적인 기능으로 제공된다.
- 일반 PC나 서버도 로컬 라우터로 이용할 수 있다.
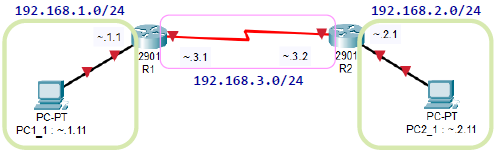
* C class 는 최대한 64개로 쪼개서 줄 수 있음
(호스트 개수가 256/64=4 이므로 첫번째랑 마지막은 네트워크 주소와 브로드캐스트주소이므로 2개의 IP 만 사용할 수 있으므로)
라우터 사이 빨강 선 : WAN에서 사용하는 시리얼 라인
정적 라우팅 실습
◾ 라우터 설정하기
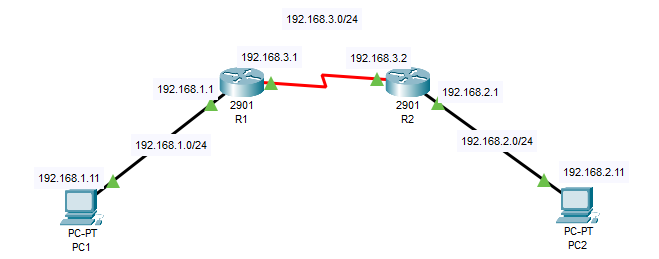
R1, R2의 IP주소를 세팅
R1(config)#int g0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R1(config-if)#int s0/0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to down
PC1에서 테스트
다른 컴퓨터로 통신이 안되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
C:\>ping 192.168.1.1
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
C:\>ping 192.168.3.1
Pinging 192.168.3.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.3.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
C:\>ping 192.168.3.2
Pinging 192.168.3.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.3.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
C:\>ping 192.168.2.11
Pinging 192.168.2.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.1: Destination host unreachable.
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
◾ 정적 라우팅 - 라우팅 정보 입력
TEST
• PC1_1에서 ~3.2까지는 연결이 가능하지만 ~2.0으로는 패킷이 전달되지 않는다.
• PC2_1에서도 ~1.0/24까지는 연결 불가다.
• R1, R2에 추가적인 라우팅 정보를 정적으로 입력해준다.
• 명령
ip route [dst IP] [dst netmask] [next_ip | exit_interface]
ex) ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
R1
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
R1(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.3.2
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 192.168.3.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R2
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 serial0/0/0
%Default route without gateway, if not a point-to-point interface, may impact performance
R2(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 192.168.3.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
PC1에서 테스트
통신이 잘 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
C:\>ping 192.168.2.11
Pinging 192.168.2.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 3ms, Maximum = 4ms, Average = 3ms
C:\>ping 192.168.2.11
Pinging 192.168.2.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=6ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 3ms, Maximum = 6ms, Average = 4ms
◾ 정적 라우팅 - Default 라우팅
Default 라우팅
• 모든 네트워크 정보를 모두 입력할 수 없음으로 기본 라우팅 정보를 입력한다.
• 명령
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [next_ip | exit_interface]
(0.0.0.0 : 모든 네트워크 정보)
ex) ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0/0
• 0.0.0.0 : 쿼드 제로 네트워크 주소및 서브넷마스크
- 라우팅 정보가 없는 모든 네트워크와 서브넷마스크를 의미한다.
- 라우팅 경로가 다중 경로인 경우 default 경로가 지정되더라도 경로 지정이 필요하다.
- 인터넷 단일 경로 라우터의 경우 매우 유용하다.
R1 라우팅
R1(config)#no ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0/0
%Default route without gateway, if not a point-to-point interface, may impact performance
R1(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 0.0.0.0 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 192.168.3.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R1
R2(config)#no ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 serial0/0/0
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0/0
%Default route without gateway, if not a point-to-point interface, may impact performance
R2(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 0.0.0.0 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 192.168.3.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
PC1에서 테스트
C:\>ping 192.168.2.11
Pinging 192.168.2.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Reply from 192.168.2.11: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 2ms, Maximum = 4ms, Average = 3ms'네트워크 공부 기록' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 동적 라우팅 및 RIP (0) | 2022.01.17 |
|---|---|
| 정적 라우팅 구현 실습 (라우팅 정보 입력 및 Default 라우팅) (0) | 2022.01.14 |
| VLAN 실습 (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| VLAN (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| STP (0) | 2022.01.11 |